Pentamidine, with the chemical formula C19H24N4O2, has the CAS number 100-33-4. It appears as a white crystalline powder with no distinct odor. Its basic structure consists of a pentamidine molecule composed of carbon, hydrogen, nitrogen, and oxygen atoms. This compound is sparingly soluble in water. Pentamidine is a medication used to treat certain types of pneumonia caused by a specific parasite. It is also used to prevent and treat a certain type of pneumonia (Pneumocystis pneumonia) in people with a weakened immune system. Pentamidine is administered through injection or inhalation. It is important to follow the dosage instructions and precautions provided by healthcare professionals when using this medication. Safety information indicates that pentamidine may cause side effects such as low blood sugar, low blood pressure, and kidney problems. It is essential to consult a healthcare professional for proper guidance and monitoring during the use of this medication.
Applicable Fields
Antiprotozoal Agent: Pentamidine is primarily used as an antiprotozoal agent. Its purpose in this field involves its ability to inhibit the growth and reproduction of certain parasites, such as Pneumocystis jirovecii. The mechanism of action in antiprotozoal activity is not fully understood, but it is believed to interfere with the DNA and RNA synthesis of the parasites, leading to their death.
Antibacterial Agent: Pentamidine has also shown antibacterial activity against certain bacteria. Its mechanism of action in this context is not well-established, but it is thought to disrupt bacterial cell membranes and inhibit essential cellular processes, ultimately leading to bacterial death.
Storage
Conditions: Store in a cool and dry place.

|

|

|
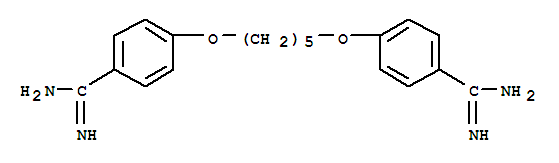
|
![Benzenecarboximidamide,4,4'-[1,5-pentanediylbis(oxy)]bis-](https://img1.guidechem.com/chem/e/dict/31/100-33-4.jpg)
|

|

|

|

|

|