-

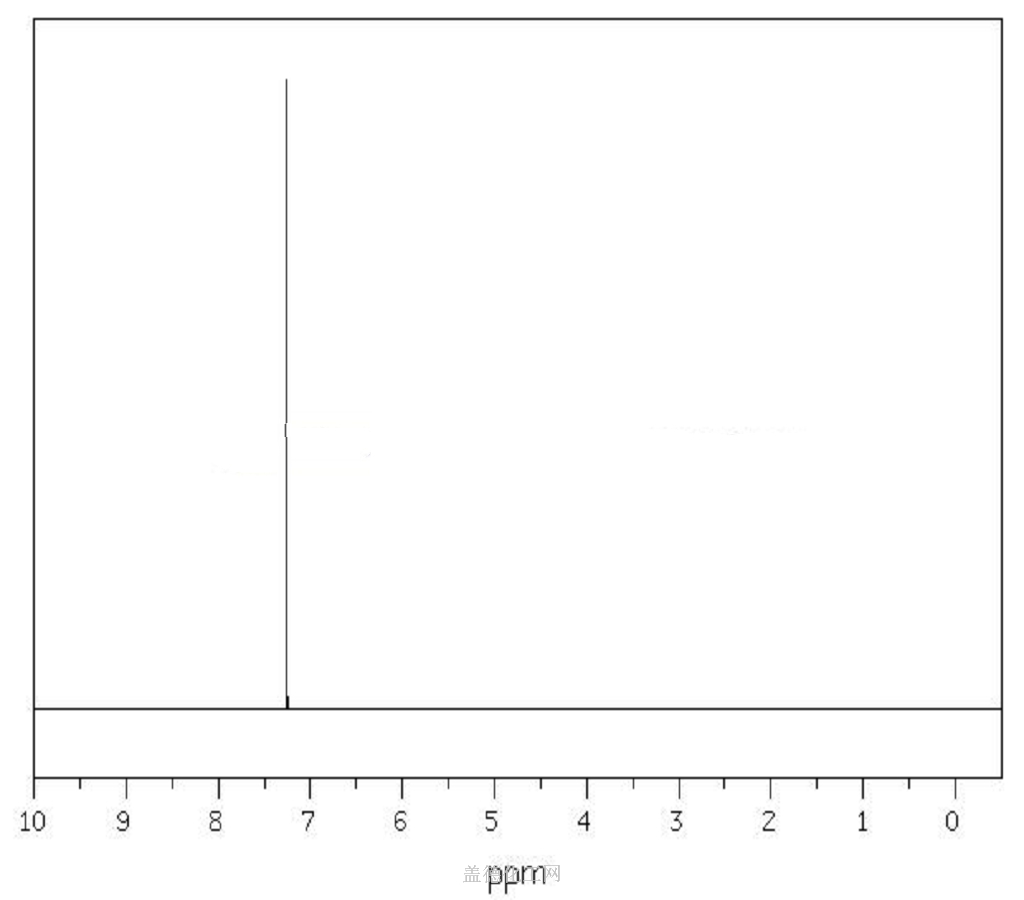
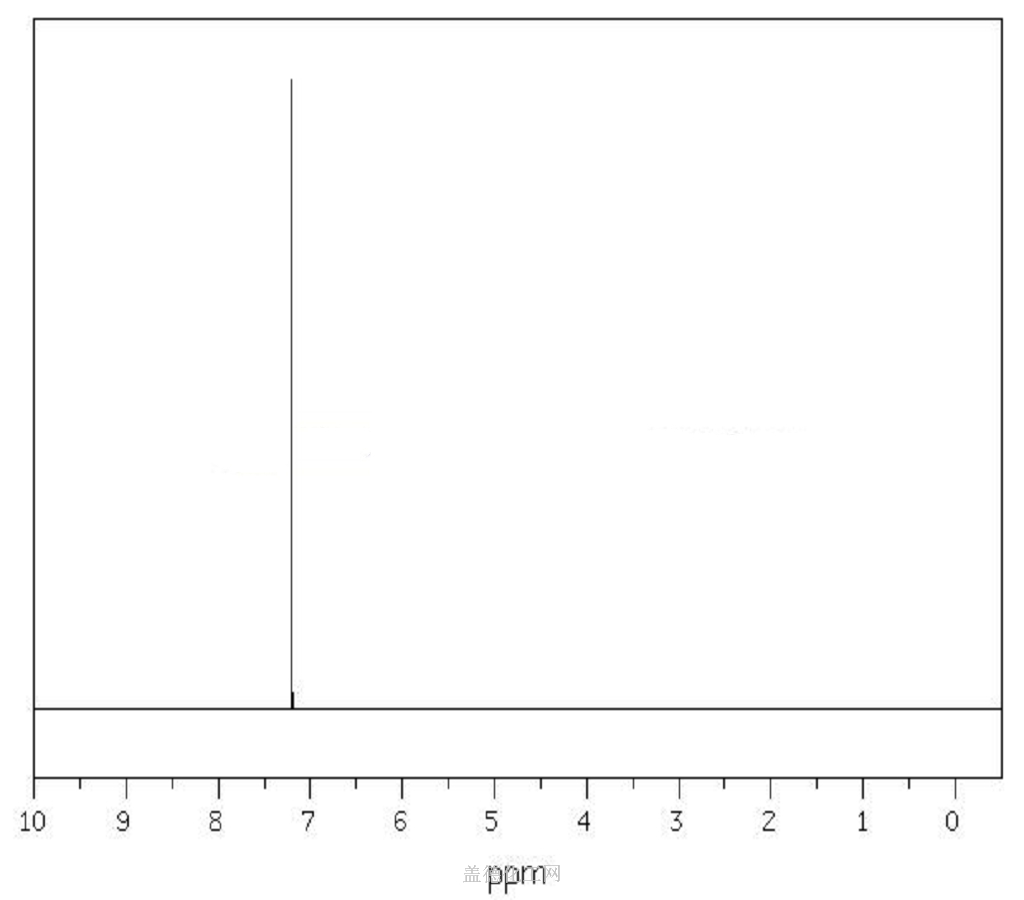
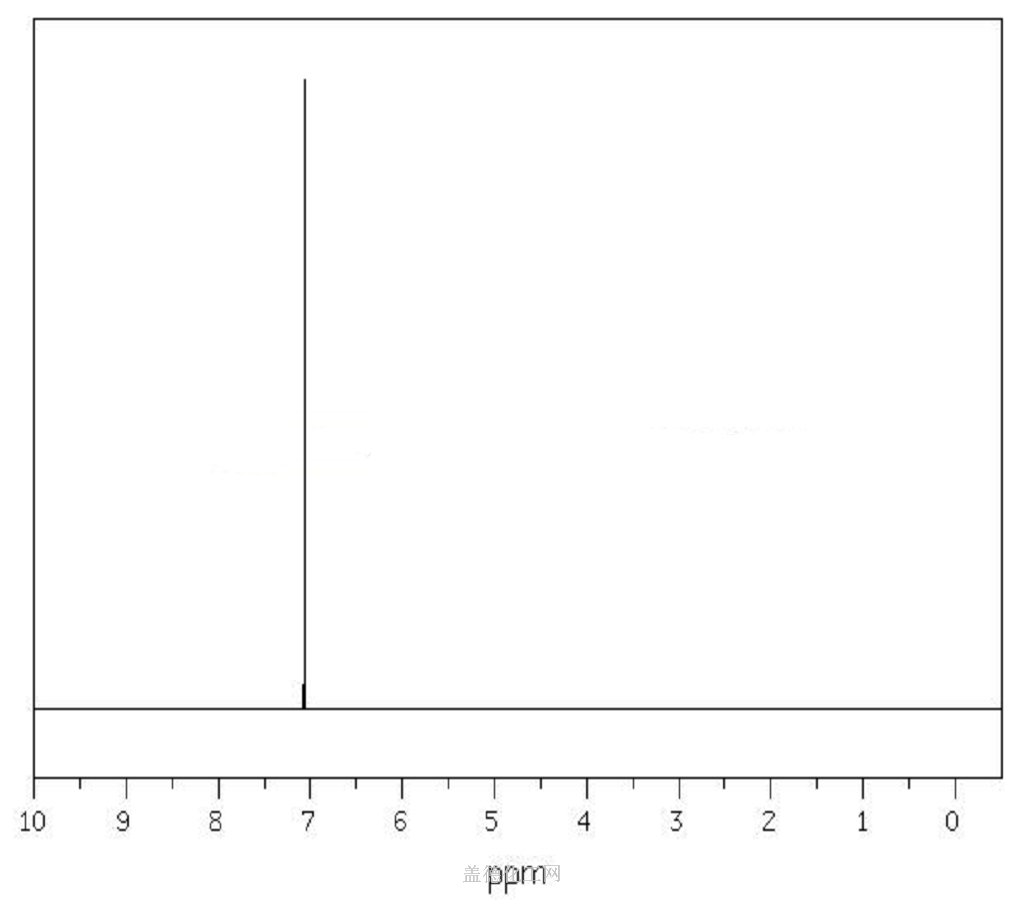
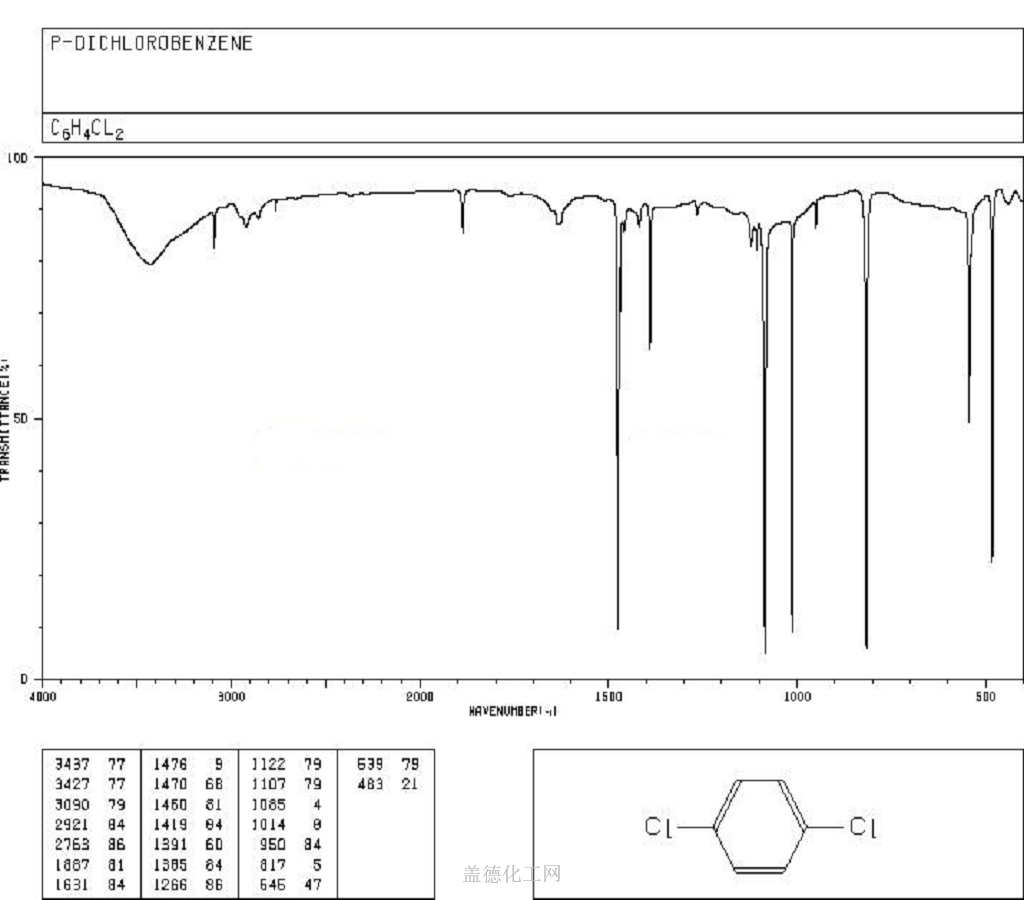
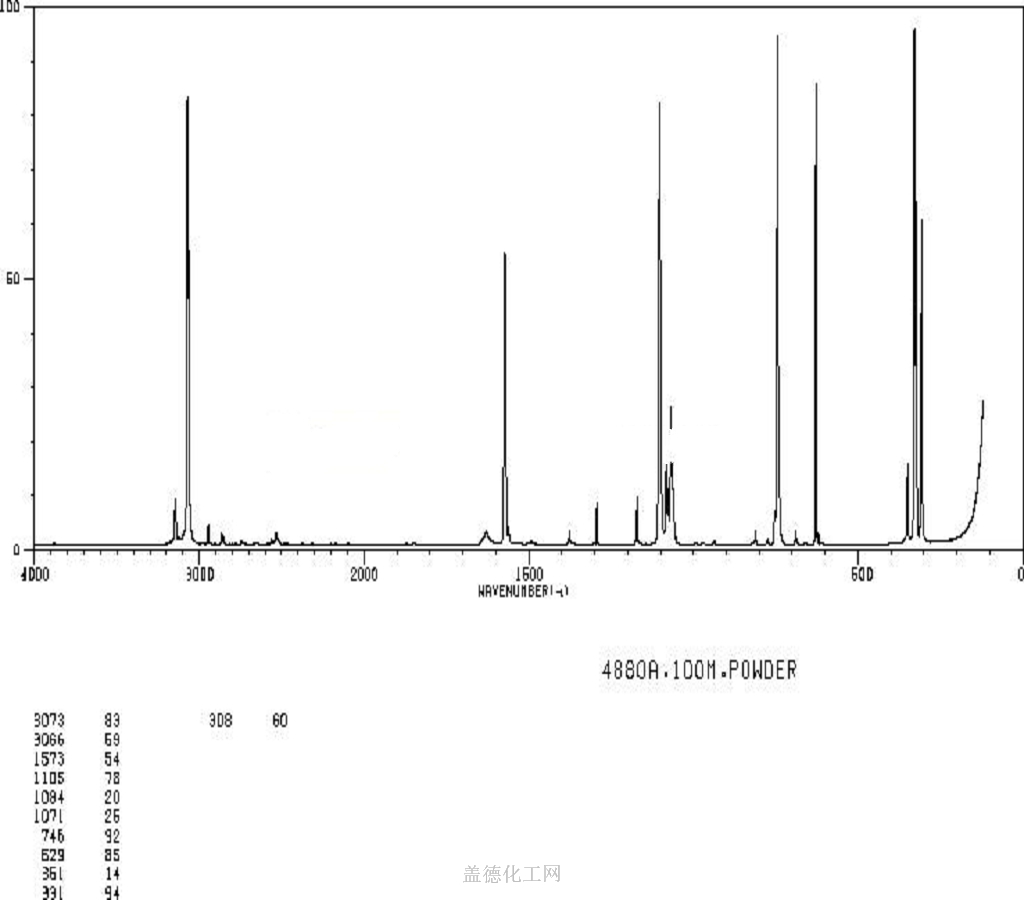
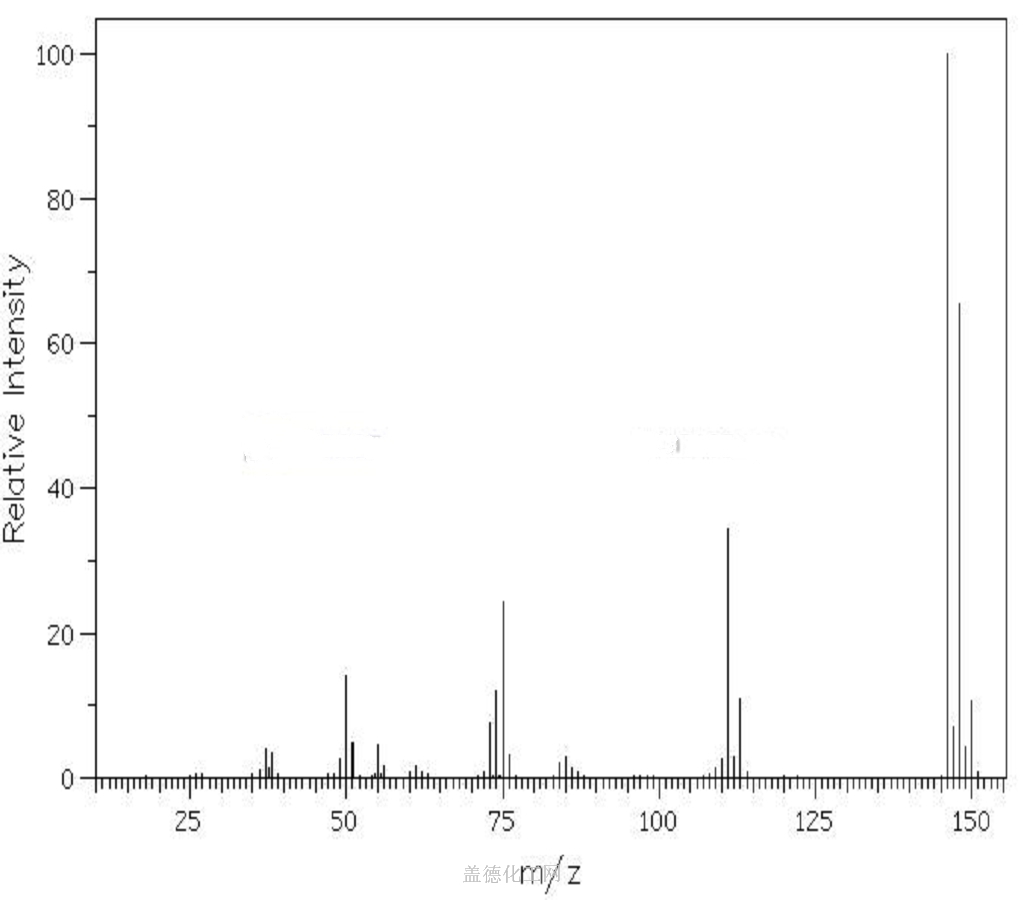
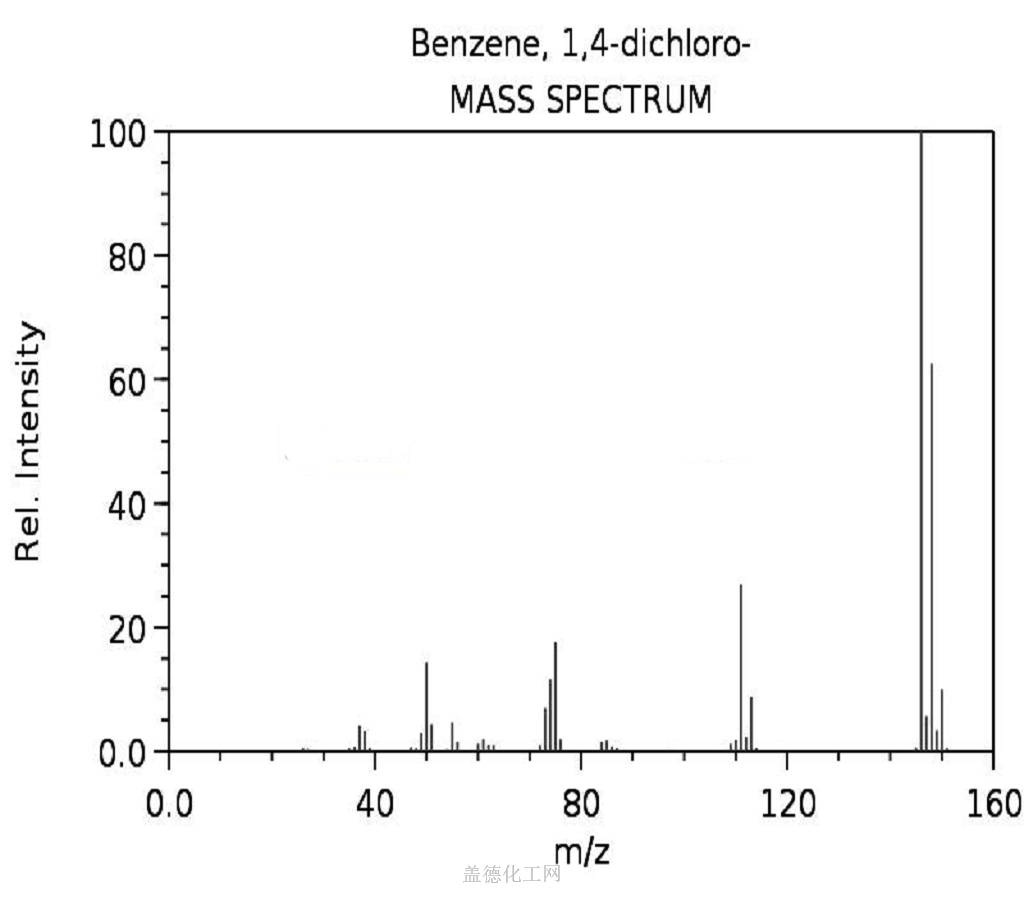
1,4-Dichlorobenzene
- CAS:106-46-7
- MW:147.00196
- MF:C6H4Cl2
- Category
Organic Intermediates Pharmaceuticals and Biochemicals Basic Organic Chemicals Agrochemicals Inorganic Chemicals Catalyst and Auxiliary Custom Manufacturing Food & Feed Additives Daily Chemicals Dyestuffs and Pigments Laboratory Chemicals Adhesives and Sealants Flavour & Fragrance Paint and Coatings Polymer Metals and Minerals
- Encyclopedia
- Dictionary
- Supplier
- Buyer Request
- TradeShow
- FAQs
- Structure Search
 EN
EN