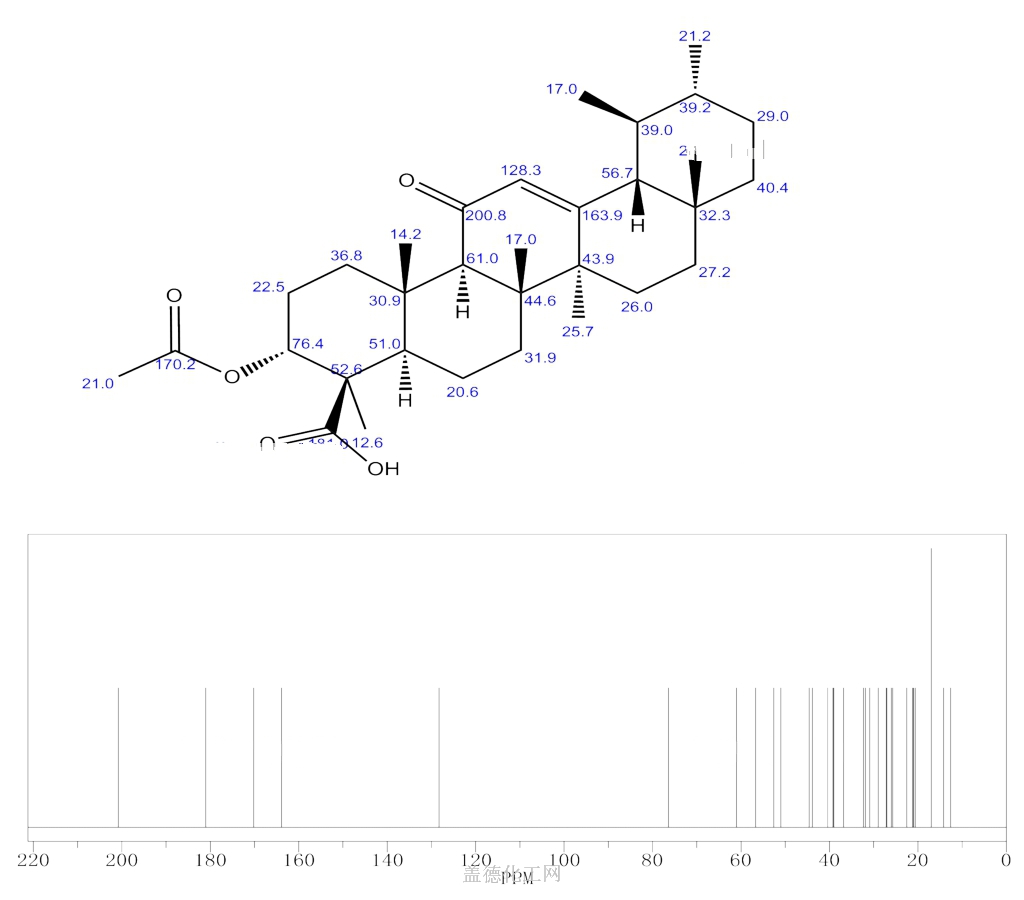
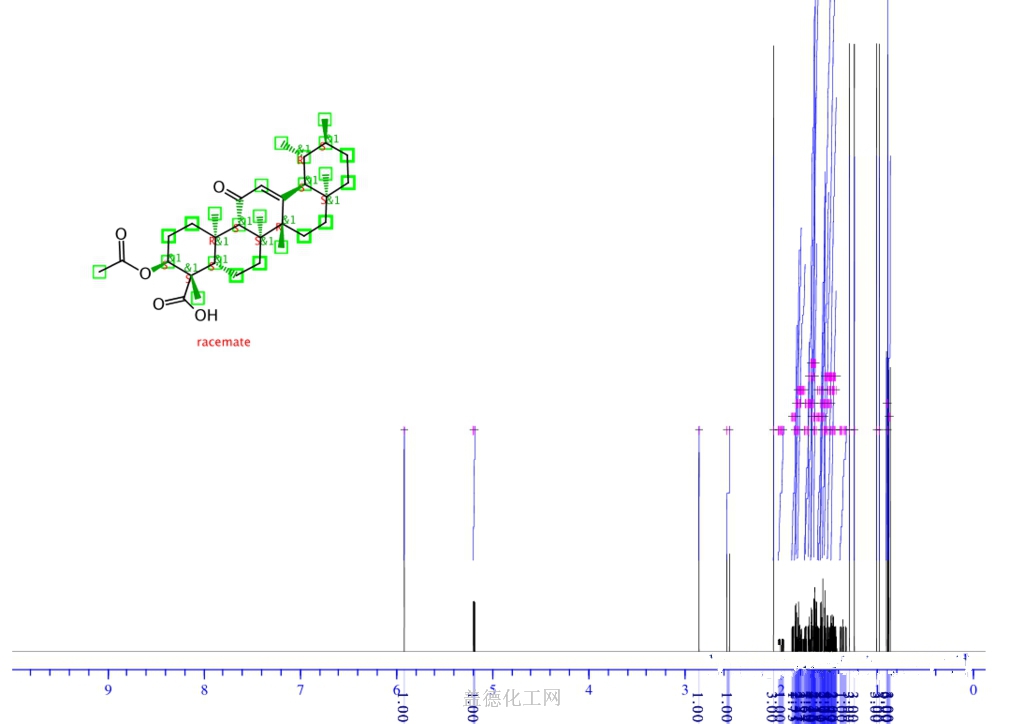
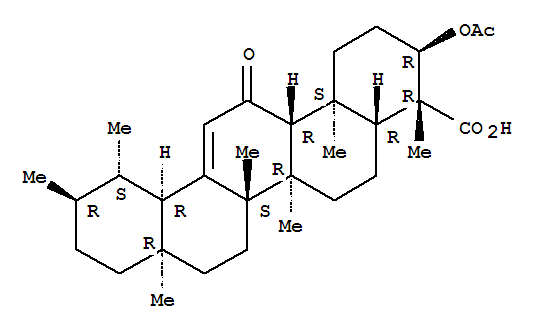
The Acetyl-11-keto-beta-boswellic acid is an organic compound with the formula C32H48O5. The systematic name of this chemical is (3α)-3-(acetyloxy)-11-oxours-12-en-24-oic acid. With the CAS registry number 67416-61-9, it is also named as urs-12-en-24-oic acid, 3-(acetyloxy)-11-oxo-, (3α)-. The product's categories are Miscellaneous Natural Products; Pharmaceuticals. Besides, it should be stored at temperature of -20 °C.
Physical properties about Acetyl-11-keto-beta-boswellic acid are: (1)ACD/LogP: 8.00; (2)# of Rule of 5 Violations: 2; (3)ACD/LogD (pH 5.5): 6.76; (4)ACD/LogD (pH 7.4): 4.97; (5)ACD/BCF (pH 5.5): 40485.62; (6)ACD/BCF (pH 7.4): 663.88; (7)ACD/KOC (pH 5.5): 30680.92; (8)ACD/KOC (pH 7.4): 503.11; (9)#H bond acceptors: 5; (10)#H bond donors: 1; (11)#Freely Rotating Bonds: 3; (12)Polar Surface Area: 69.67 Å2; (13)Index of Refraction: 1.549; (14)Molar Refractivity: 143.22 cm3; (15)Molar Volume: 450.1 cm3; (16)Polarizability: 56.77×10-24cm3; (17)Surface Tension: 45.7 dyne/cm; (18)Density: 1.13 g/cm3; (19)Flash Point: 184.4 °C; (20)Enthalpy of Vaporization: 97.58 kJ/mol; (21)Boiling Point: 600.3 °C at 760 mmHg; (22)Vapour Pressure: 5.85E-16 mmHg at 25°C.
When you are using this chemical, please be cautious about it as the following:
This chemical is irritating to eyes, respiratory system and skin. In case of contact with eyes, rinse immediately with plenty of water and seek medical advice.
You can still convert the following datas into molecular structure:
(1)SMILES: O=C(O)[C@@]1(C)[C@H](OC(=O)C)CC[C@@]3(C)[C@H]1CC[C@]2([C@]5(/C(=C\C(=O)[C@@H]23)[C@@H]4[C@H]([C@@H](CC[C@]4(C)CC5)C)C)C)C
(2)InChI: InChI=1/C32H48O5/c1-18-9-12-28(4)15-16-30(6)21(25(28)19(18)2)17-22(34)26-29(5)13-11-24(37-20(3)33)32(8,27(35)36)23(29)10-14-31(26,30)7/h17-19,23-26H,9-16H2,1-8H3,(H,35,36)/t18-,19+,23-,24-,25+,26-,28-,29+,30-,31-,32-/m1/s1
(3)InChIKey: HMMGKOVEOFBCAU-BCDBGHSCBM
(4)Std. InChI: InChI=1S/C32H48O5/c1-18-9-12-28(4)15-16-30(6)21(25(28)19(18)2)17-22(34)26-29(5)13-11-24(37-20(3)33)32(8,27(35)36)23(29)10-14-31(26,30)7/h17-19,23-26H,9-16H2,1-8H3,(H,35,36)/t18-,19+,23-,24-,25+,26-,28-,29+,30-,31-,32-/m1/s1
(5)Std. InChIKey: HMMGKOVEOFBCAU-BCDBGHSCSA-N

 EN
EN