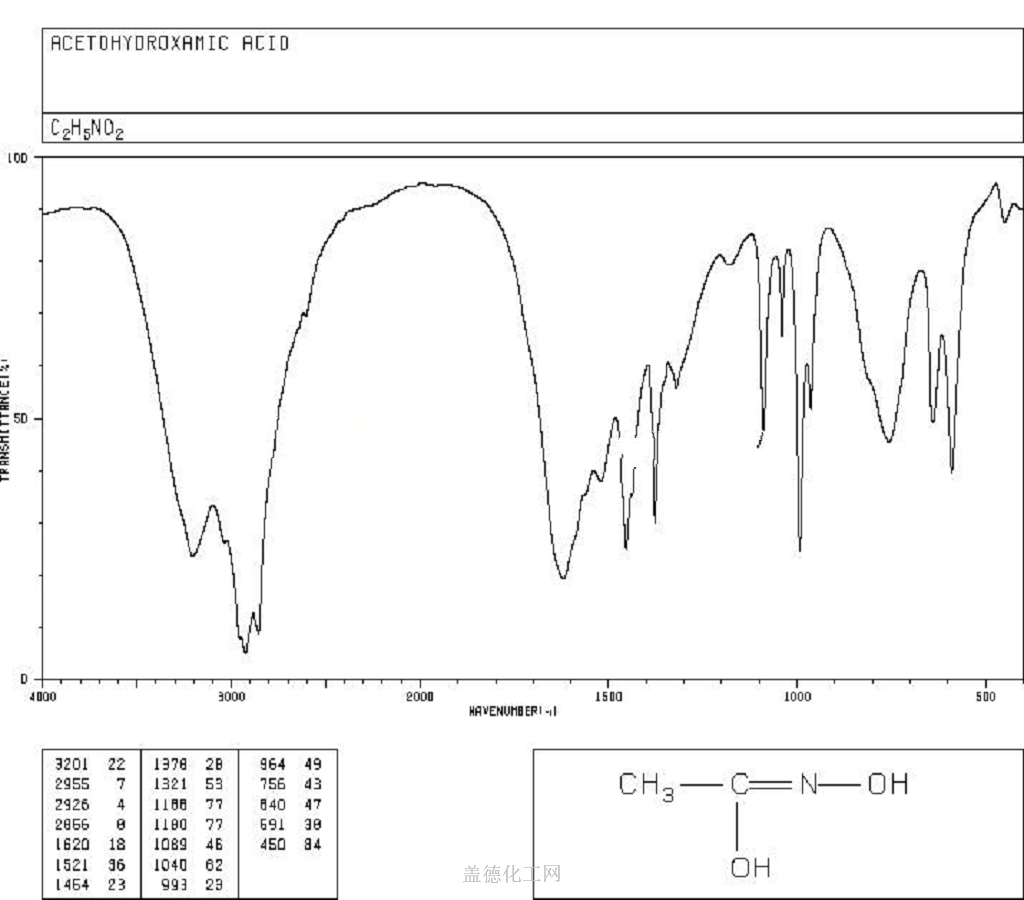
Acetohydroxamic acid is a potent, non-competitive and irreversible inhibitor ofbacterial urease (Ki≈lO-7M). This enzyme, which is widely distributed in plantsand bacteria, but not in mammalian cells, catalyzes the decomposition of urea toammonia. Elevated urinary ammonia levels can reduce the antibacterial effectivenessof a number of agents. Thus, acetohydroxamic acid is useful as adjunctivetherapy to decrease urinary ammonia and alkalinity in patients with chronicurea-splitting urinary infection. Such infections are a leading cause of recurringcomplications and death in paraplegics.
View more+
1. Names and Identifiers
2. Properties
3. Use and Manufacturing
4. Safety and Handling
5. MSDS
6. NMR Spectrum
7. Synthesis Route
8. Precursor and Product
9. Computed Properties
12. Related Questions
13. Realated Product Infomation

 EN
EN

 T
T