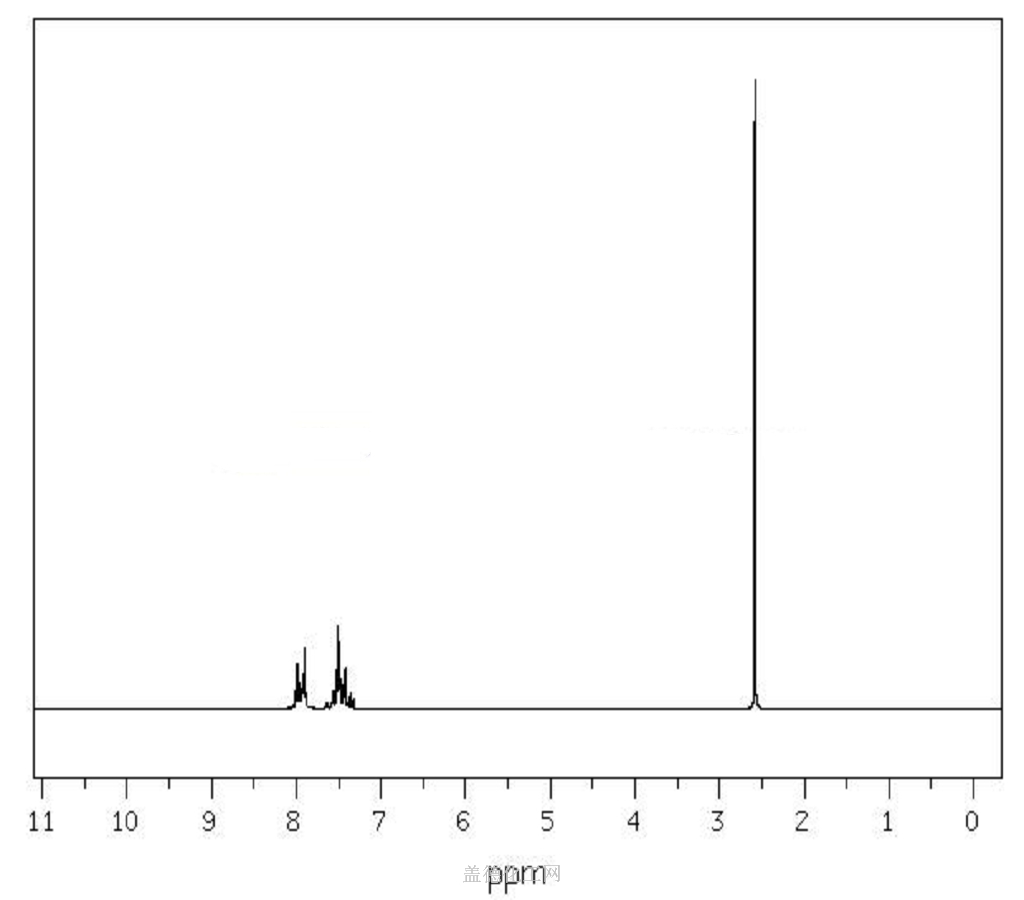
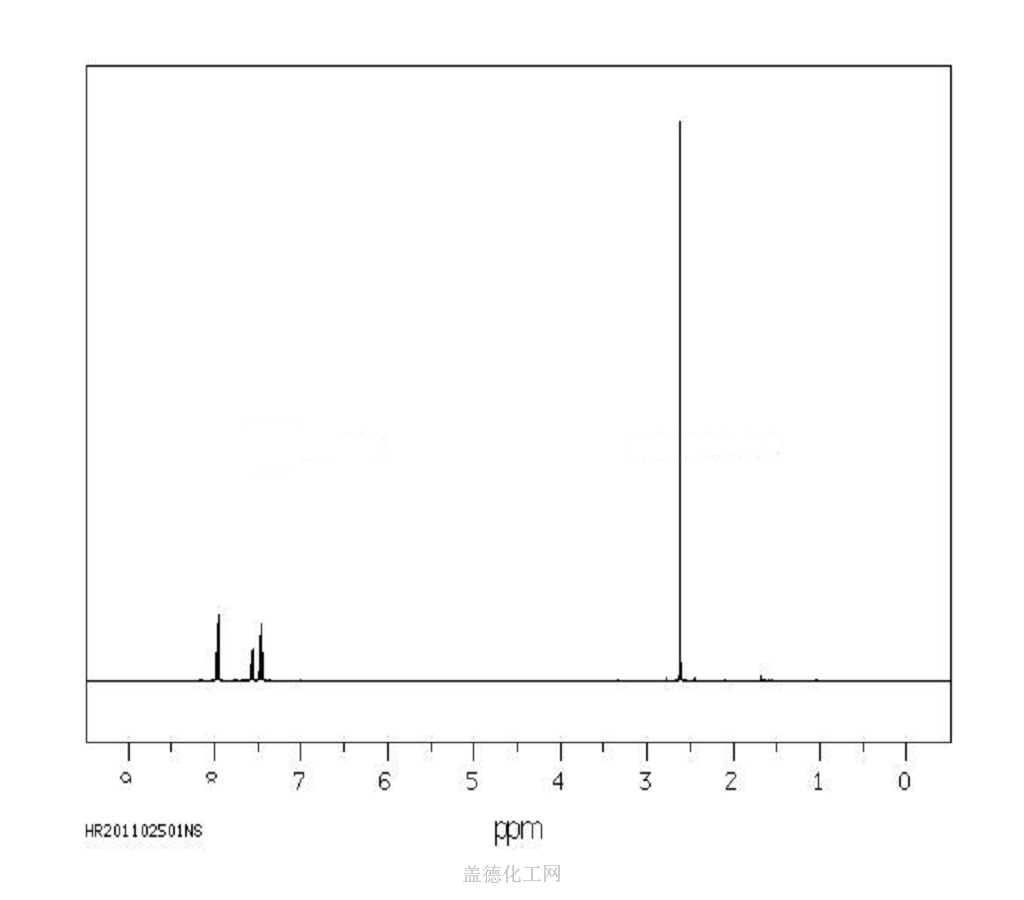
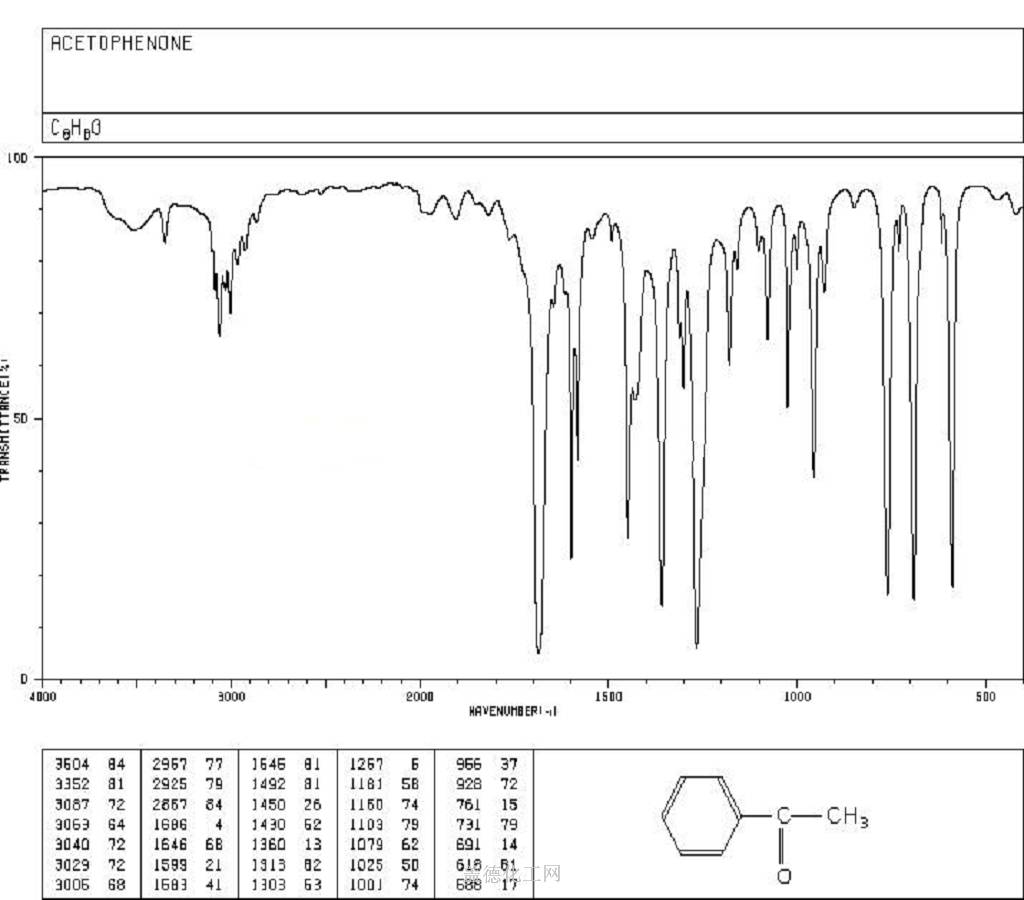
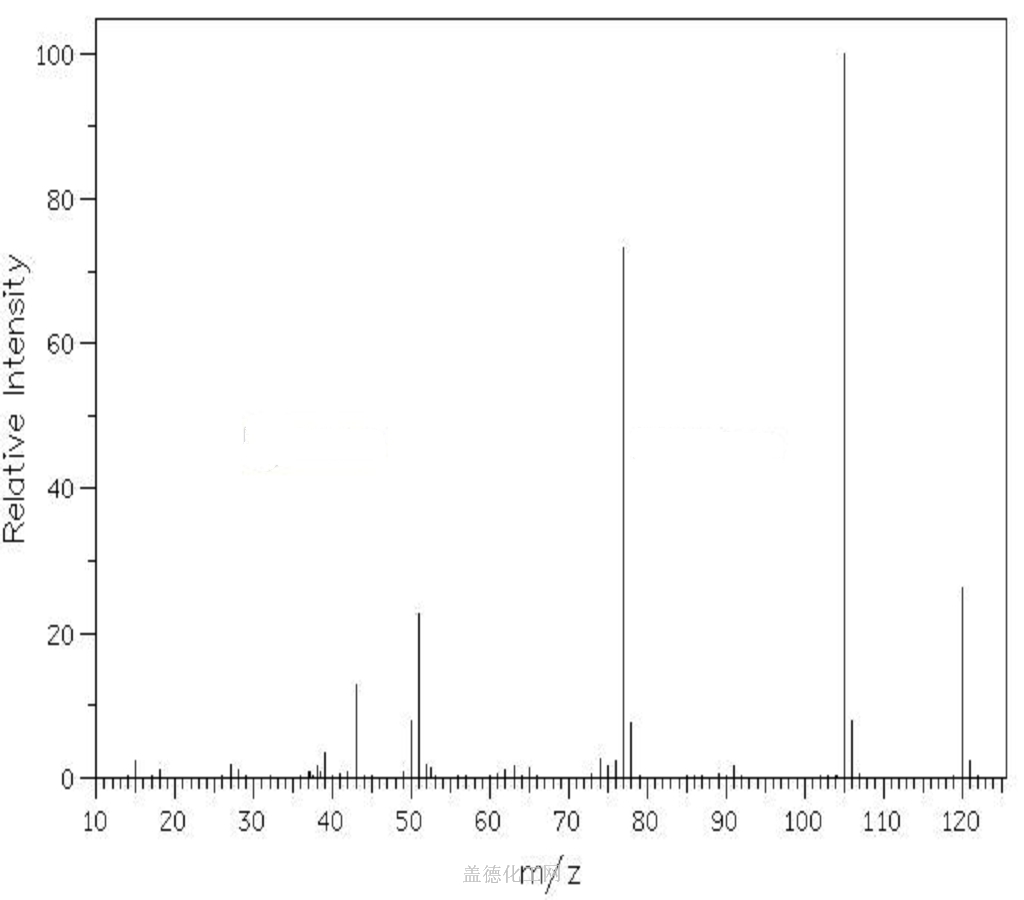
Acetophenone, with the chemical formula C8H8O and CAS registry number 98-86-2, is a compound known for its aromatic fragrance and use in various industries. This colorless liquid, also referred to as phenyl methyl ketone, is characterized by its carbonyl group attached to a phenyl ring. It is commonly used as a solvent, flavoring agent, and intermediate in the production of pharmaceuticals, dyes, and perfumes. Acetophenone has been studied for its potential antimicrobial and antioxidant properties. It is an important compound in the field of organic chemistry and chemical synthesis, contributing to the development of new materials and compounds.
View more+
1. Names and Identifiers
2. Properties
3. Use and Manufacturing
4. Safety and Handling
5. MSDS
6. NMR Spectrum
7. Synthesis Route
8. Precursor and Product
9. Computed Properties
12. Related Questions
13. Realated Product Infomation

 EN
EN

 Xn,?
Xn,? T,?
T,? F
F