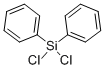
The?IUPAC name of this chemical is?dichloro(diphenyl)silane. With?the?CAS registry number 80-10-4,?it is also named as Benzene, 1,1'-(dichlorosilylene)bis-.?The product's categories are?Silicon Compounds; Organosilicon Reagents; Dichlorosilanes; Dichlorosilanes (for Polysilanes); Functional Materials; Reagent for High-Performance Polymer Research; Si-Cl Compounds; Phenyl Silanes.?It is colorless transparent liquid?with a pungent odor that?is corrosive to metals and tissue.?In addition, this chemical will burn though?it may require some effort to ignite.?When heated to decomposition or on contact with acid or acid fumes it emits toxic fumes of Cl-.?So the storage environment should be ventilate, low-temperature and dry.
The other characteristics of this product can be summarized as:?(1)ACD/LogP: 6.69; (2)# of Rule of 5 Violations: 1; (3)ACD/LogD (pH 5.5): 6.69; (4)ACD/LogD (pH 7.4): 6.69; (5)#H bond acceptors: 0; (6)#H bond donors: 0; (7)#Freely Rotating Bonds: 2; (8)Index of Refraction: 1.582; (9)Molar Refractivity: 69.88 cm3; (10)Molar Volume: 209.2 cm3; (11)Polarizability: 27.7×10-24 cm3; (12)Surface Tension: 36.7 dyne/cm; (13)Enthalpy of Vaporization: 52.36 kJ/mol; (14)Boiling Point: 305 °C at 760 mmHg; (15)Vapour Pressure: 0.00152 mmHg at 25°C; (16)Rotatable Bond Count: 2; (17)Exact Mass: 251.992882; (18)MonoIsotopic Mass: 251.992882; (19)Heavy Atom Count: 15; (20)Complexity: 174.
Preparation of Dichloro diphenylsilane:?The crude monomer can be obtained by chlorobenzene and silica powder in the presence of copper catalyst. Then we can get?trichloro(phenyl)silane and dichloro diphenylsilane by?rectification.
Uses of Dichloro diphenylsilane:?It is used as raw? materials of silicone oil and silicone. it is also used in the production of silicone and siloxanes and silicones, methyl phenyl. In addition, it can?react with?biphenyl-2,2'-diol to get 6,6-diphenyl-dibenzo[d,f][1,3,2]dioxasilepine. This reaction needs solvent?benzene?by heating.
When you are using this chemical, please be cautious about it as the following:
It is not only harmful if swallowed, but also toxic in contact with skin.?In case of contact with eyes, rinse immediately with plenty of water and seek medical advice.?After contact with skin, wash immediately with plenty of soap-suds.?If you want to contact this product, you must wear suitable protective clothing, gloves and eye/face protection.?In case of accident or if you feel unwell, seek medical advice immediately (show the label whenever possible.)?
People can use the following data to convert to the molecule structure.?
1. SMILES:Cl[Si](Cl)(c1ccccc1)c2ccccc2
2.?InChI:InChI=1/C12H10Cl2Si/c13-15(14,11-7-3-1-4-8-11)12-9-5-2-6-10-12/h1-10H
The following are the toxicity data which has been tested.
| Organism |
Test Type |
Route |
Reported Dose (Normalized Dose) |
Effect |
Source |
| rabbit |
LD50 |
skin |
100uL/kg (0.1mL/kg) |
BEHAVIORAL: SOMNOLENCE (GENERAL DEPRESSED ACTIVITY)
SKIN AND APPENDAGES (SKIN): "DERMATITIS, OTHER: AFTER SYSTEMIC EXPOSURE" |
National Technical Information Service. Vol. OTS0571886, |

 EN
EN