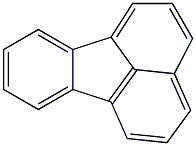
Fluoranthene, with the chemical formula C16H10 and CAS registry number 206-44-0, is a polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon (PAH) compound. It is a colorless solid that is insoluble in water but soluble in organic solvents. Fluoranthene is commonly found in coal tar, crude oil, and various combustion products. It is also produced during the incomplete combustion of organic materials, such as wood and fossil fuels. Fluoranthene is considered to be a potential environmental pollutant and is classified as a possible human carcinogen by the International Agency for Research on Cancer (IARC). It is important to handle and dispose of fluoranthene properly to minimize its impact on human health and the environment.
View more+
1. Names and Identifiers
2. Properties
3. Use and Manufacturing
4. Safety and Handling
5. MSDS
6. NMR Spectrum
7. Synthesis Route
8. Precursor and Product
9. Computed Properties
12. Realated Product Infomation

 EN
EN

 Xn;
Xn; N;
N; F;
F; T
T