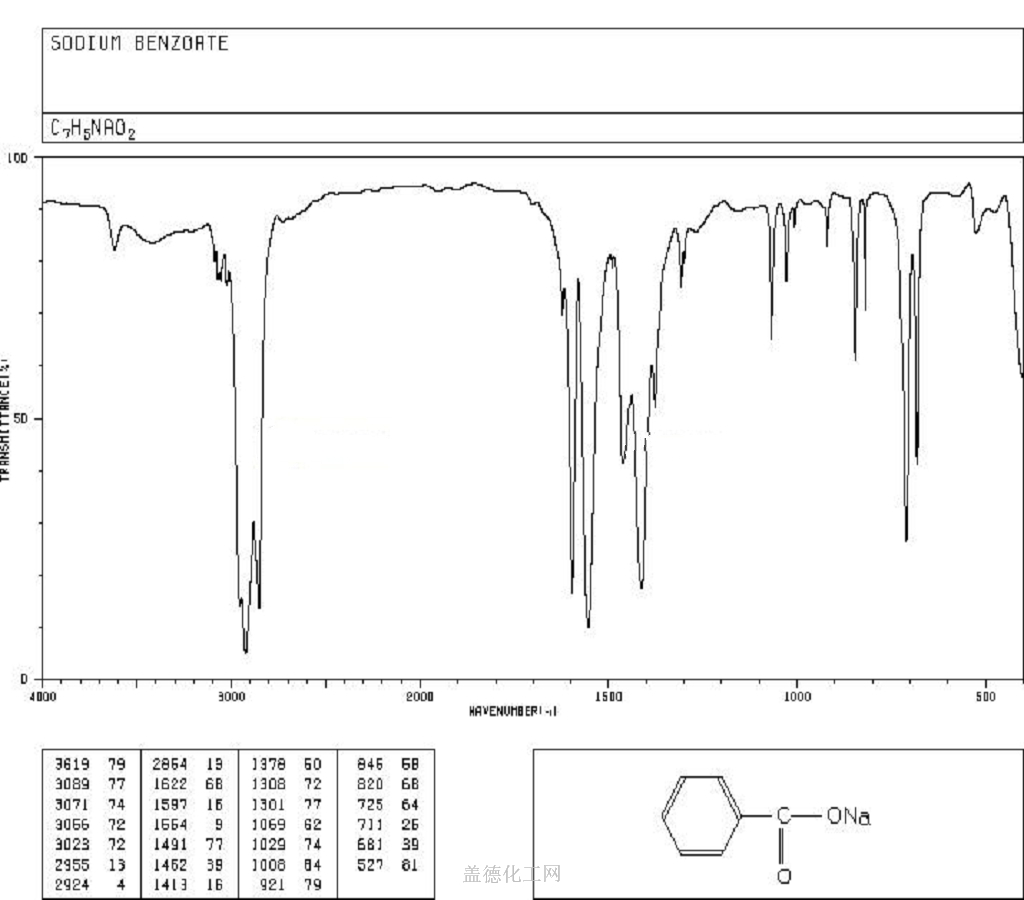
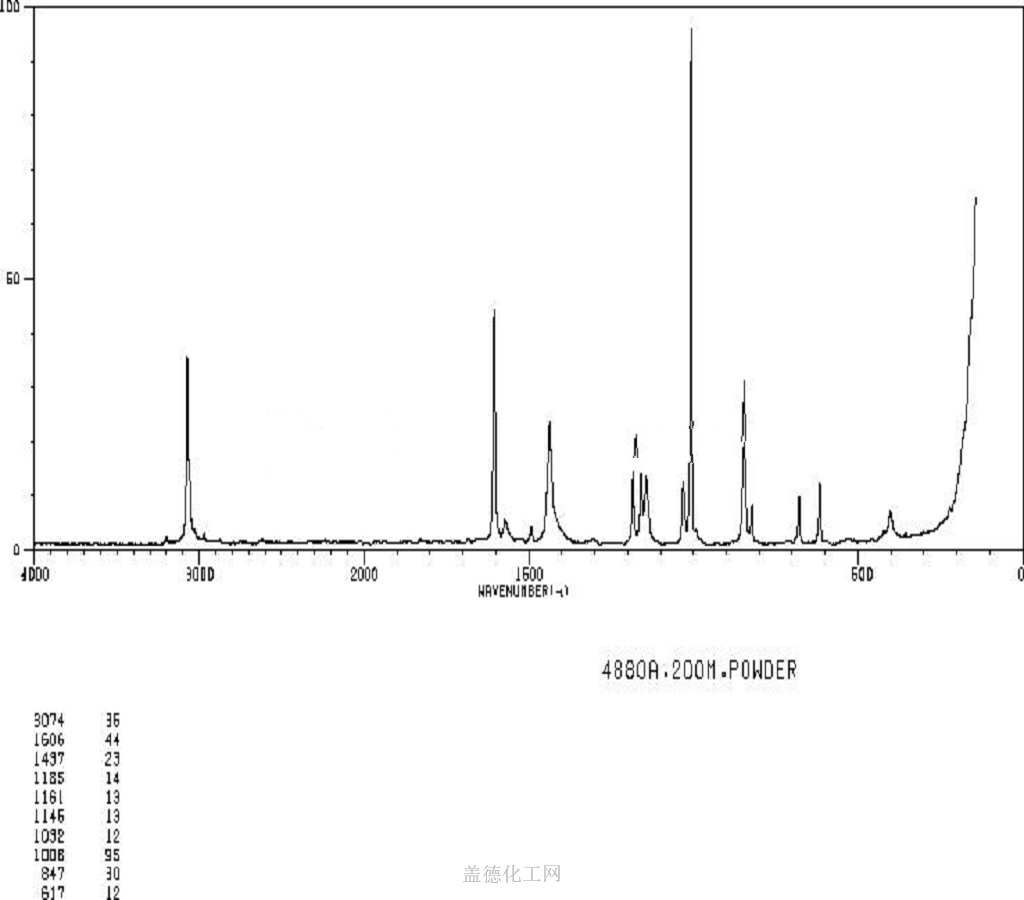
Sodium benzoate, with the chemical formula C7H5NaO2 and CAS registry number 532-32-1, is a compound commonly used as a food preservative. It is a white crystalline powder that is soluble in water. Sodium benzoate is known for its ability to inhibit the growth of bacteria, yeast, and mold, making it an effective preservative for a wide range of food and beverage products. It is often used in soft drinks, fruit juices, pickles, and condiments. In addition to its preservative properties, sodium benzoate is also used as a pH adjuster and flavoring agent in some products. While generally recognized as safe by regulatory authorities, some individuals may be sensitive to sodium benzoate and may experience adverse reactions. Overall, sodium benzoate plays a crucial role in ensuring the safety and shelf life of many food and beverage products.
View more+
1. Names and Identifiers
2. Properties
3. Use and Manufacturing
4. Safety and Handling
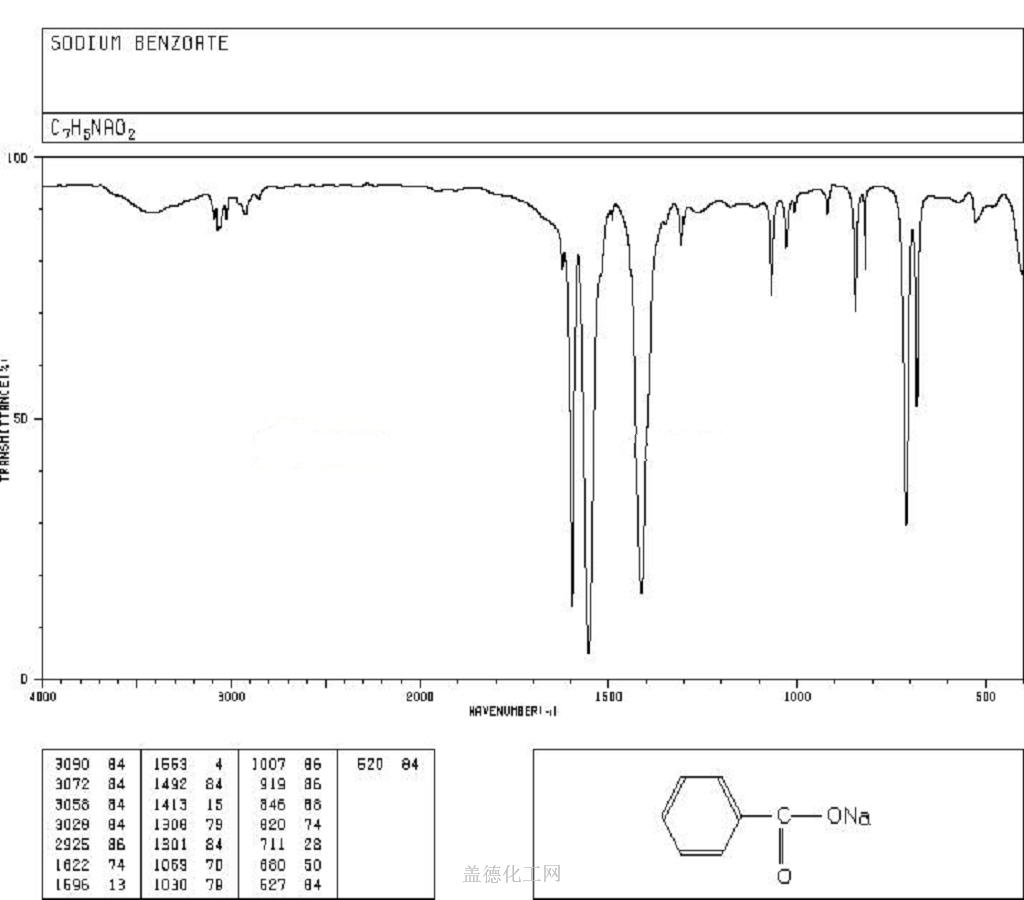
5. MSDS
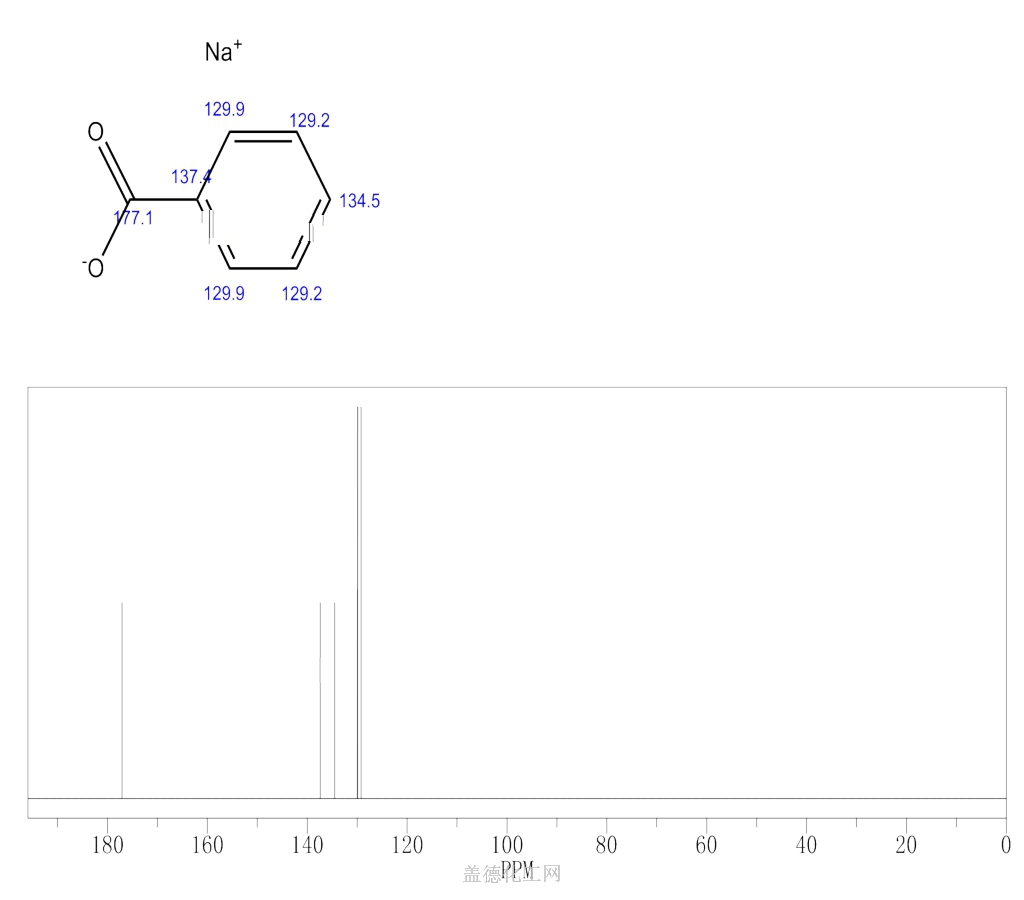
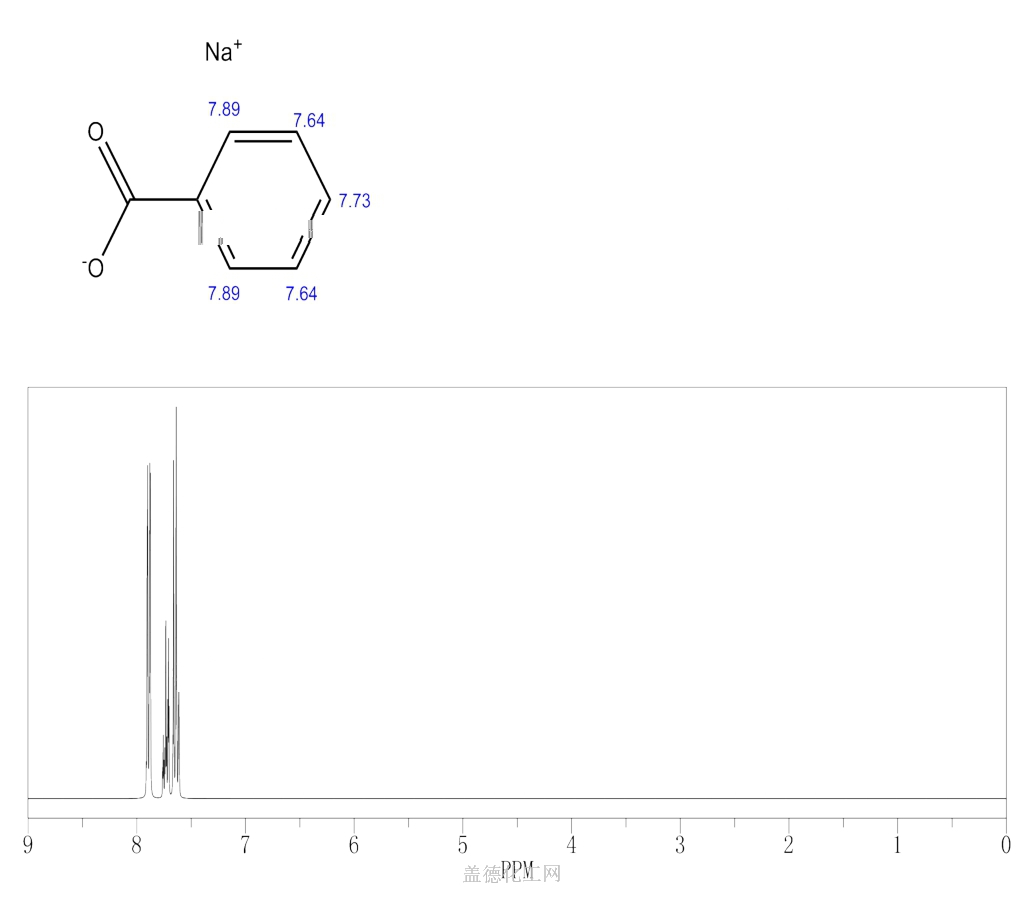
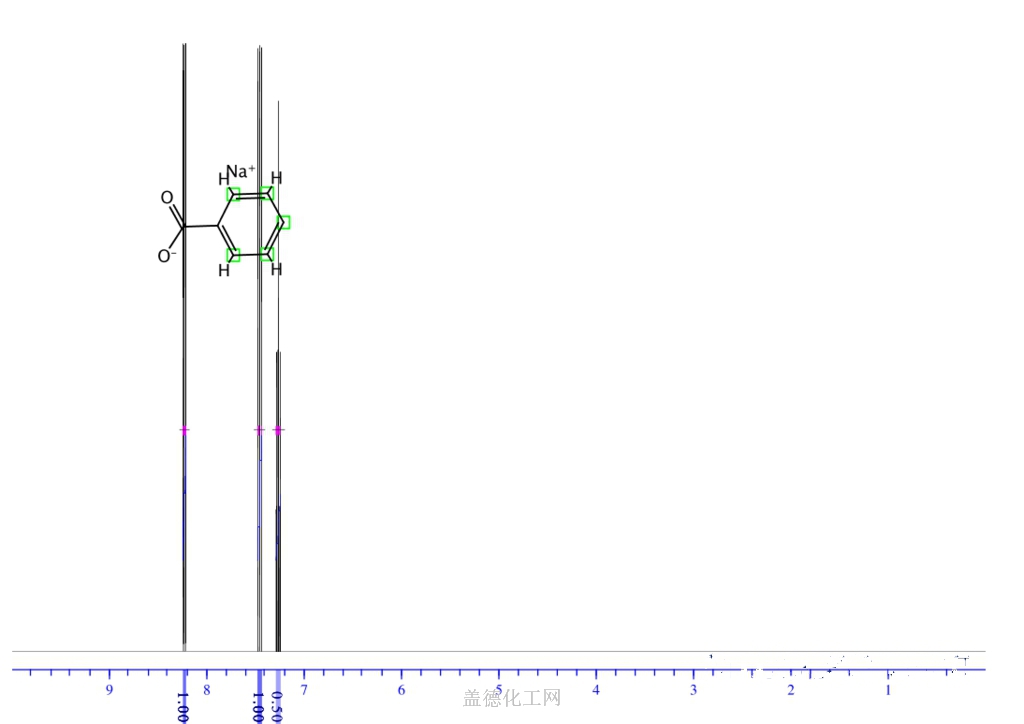
6. NMR Spectrum
7. Synthesis Route
8. Precursor and Product
9. Computed Properties
12. Related Questions
13. Realated Product Infomation

 EN
EN

 Xi
Xi