Benzene, a liquid hydrocarbon molecule, contains a unique benzene ring composed of six carbon atoms in a hexagonal configuration with alternating single and double bonds, giving it its aromatic nature.
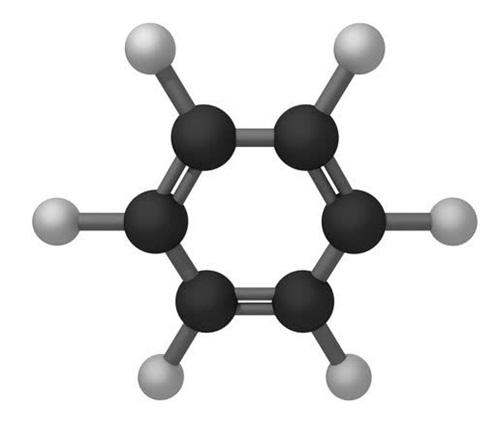
Polarity of Benzene
With a symmetric and planar structure, benzene has equal and opposing dipoles that cancel each other out, making it a nonpolar molecule.
Chemical Properties of Benzene
1. The delocalization of electrons in the ring makes benzene highly stable, leading to its aromatic nature.
2. Due to its stability, benzene undergoes substitution reactions rather than addition processes, replacing hydrogen atoms on the ring with other atoms or groups.
3. Benzene is hydrophobic, not readily dissolving in water due to its nonpolar nature.
4. It serves as a good solvent for organic compounds and is used in various industrial processes like polymer, plastic, dye, and medicine production.
5. While generally stable, benzene can react under certain conditions, such as with halogens to form halogenated derivatives.
6. Considered hazardous and a carcinogen, long-term exposure to high concentrations of benzene can lead to health issues like leukemia and bone marrow suppression.




