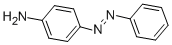This azoic coloring can be reduced in paraphenylenediamine(PPD). It ean be found in some semipermanenthair dyes, and patch tests are frequentlypositive (about 30%) in hairdressers with handdermatitis. Because of cross-sensitivity, the detectionof sensitization to p-aminoazobenzene may be assumedby a PPD test.
View more+
1. Names and Identifiers
2. Properties
3. Use and Manufacturing
4. Safety and Handling
5. MSDS
6. NMR Spectrum
7. Synthesis Route
8. Precursor and Product
9. Computed Properties
12. Realated Product Infomation

 EN
EN