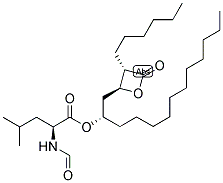
Orlistat, with the chemical formula C29H53NO5 and CAS registry number 96829-58-2, is a compound known for its use as an anti-obesity medication. It works by inhibiting the absorption of dietary fats in the body, leading to weight loss. Orlistat is commonly prescribed as a treatment for obesity and is available in both prescription and over-the-counter forms. It is typically taken orally and is most effective when used in conjunction with a reduced-calorie diet and exercise. Common side effects of Orlistat include gastrointestinal issues such as oily spotting, flatulence, and fecal urgency. It is important to note that Orlistat should not be used by individuals with certain medical conditions or during pregnancy. Overall, Orlistat is a widely used compound in the management of obesity, offering a potential solution for individuals looking to achieve weight loss goals.
View more+
1. Names and Identifiers
2. Properties
3. Use and Manufacturing
4. Safety and Handling
5. MSDS
6. NMR Spectrum
7. Computed Properties
10. Related Questions
11. Realated Product Infomation

 EN
EN