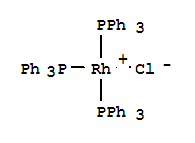-
Tris(triphenylphosphine)rhodiu
Tris(triphenylphosphine)rhodium(I) chloride, with the chemical formula C54H45ClP3Rh and CAS registry number 14694-95-2, is a compound known for its applications in catalysis and coordination chemistry. This complex, also referred to as Wilkinson's catalyst, consists of a rhodium atom coordinated to three triphenylphosphine ligands and a chloride ion. It is commonly used as a homogeneous catalyst for various organic transformations, including hydrogenation, hydroformylation, and carbonylation reactions. Tris(triphenylphosphine)rhodium(I) chloride exhibits high stability and reactivity, making it a valuable tool in synthetic chemistry. Its versatile nature and wide range of applications have contributed to its popularity in the field of organometallic chemistry.
View more+
1. Names and Identifiers
2. Properties
3. Use and Manufacturing
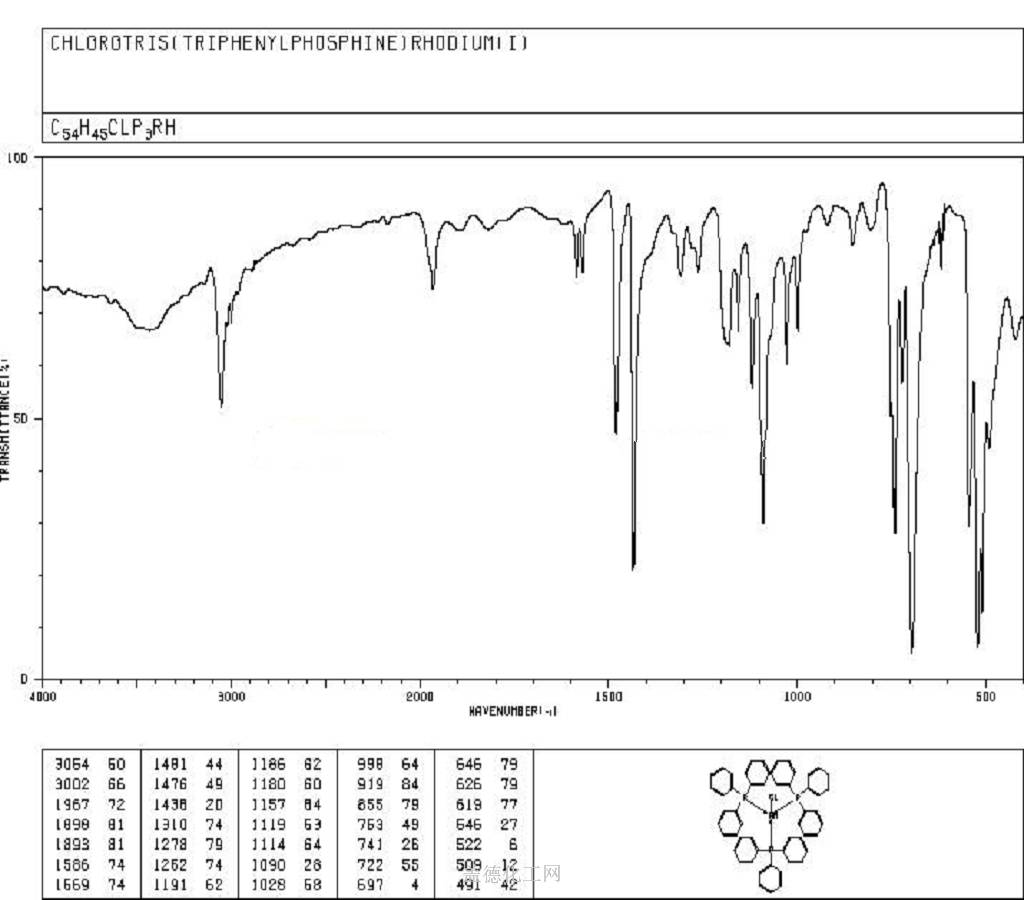
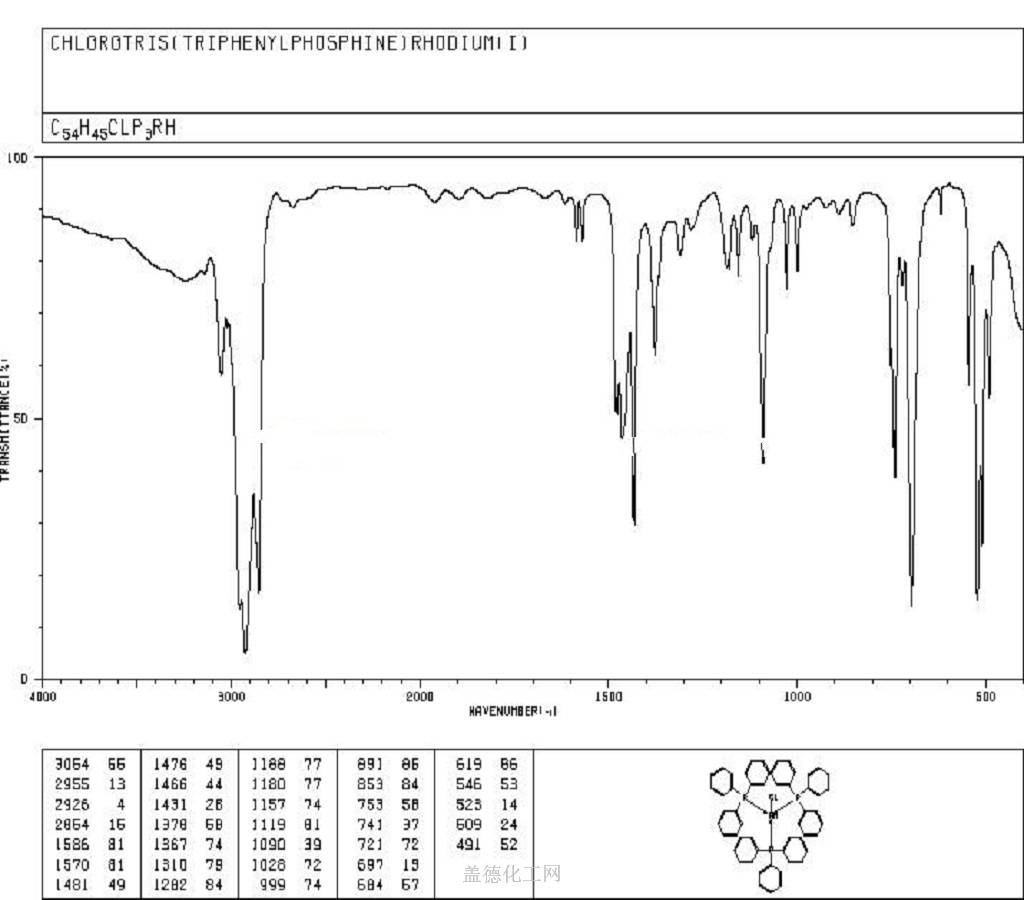
4. MSDS
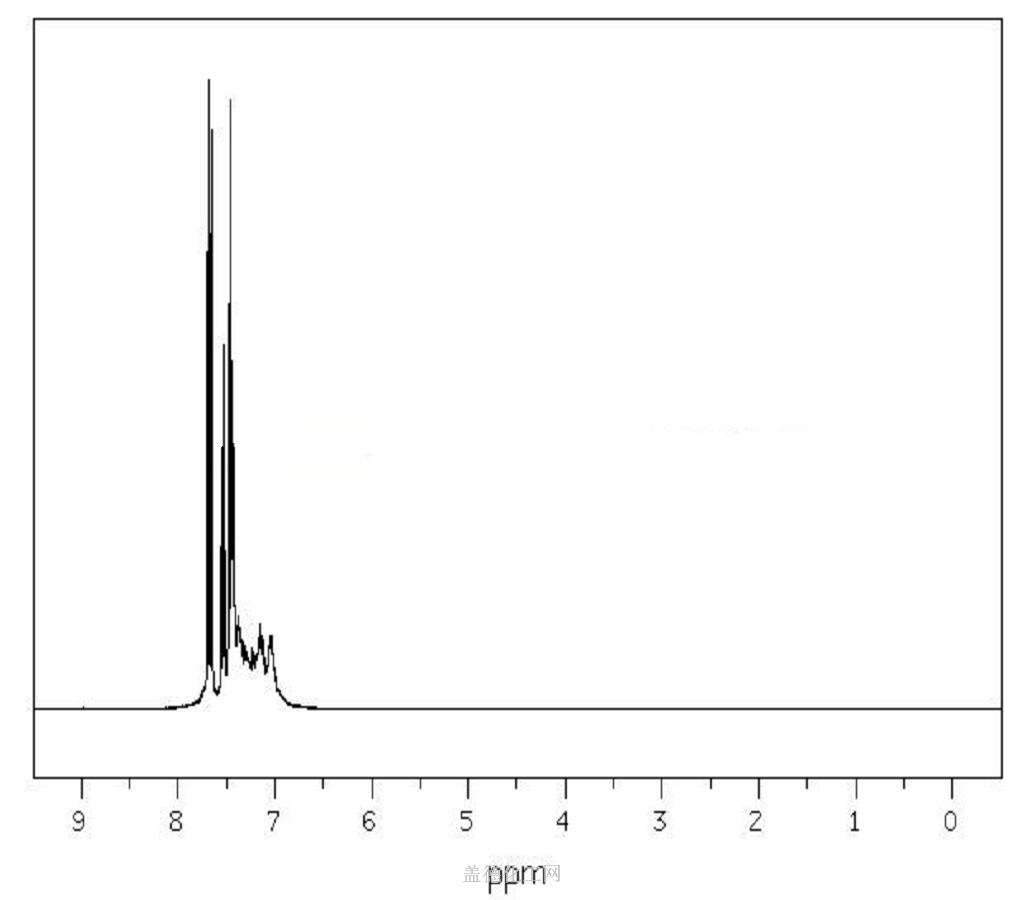
5. NMR Spectrum
6. Synthesis Route
7. Precursor and Product
8. Computed Properties
11. Related Questions
12. Realated Product Infomation

 EN
EN